 Case Studies
Case Studies
1. Measurement Details
- Measurement Date
February 11, 2019 - Measurement Devices
1. LAN-XI Data Acquisition Hardware
– Brüel & Kjæ r 3050-A-040 (Serial Number: 3050-111438)
2. Data Analysis Software
– Brüel & Kjæ r PULSE LAB SHOP 22
3. Sensors
– PCB Accelerometer
– Model: 393B05 (Serial Number: 48995, 40626) - Measurement Location
4st Floor - Measurement Setup
Bandwidth: 0 – 100 Hz
Lines: 400
Window: Hanning
Averaging: Fast Fourier Transform Spectrum Averaging
Amplitude Units: m/s2
Spectral Unit: RMS
2. Equipment Information
- Manufacturer
Thermofisher Scientific - Model
PRISMA E SEM - Floor Vibration Specification
VC-E in Vertical and Horizontal Axis
3. Vibration Isolation System Information
Model: DVIA-MB1000

| Model | DVIA-MB1000 | DVIA-MB3000 | DVIA-MB6000 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform Dimensions (L x W x H) | Custom-made | |||
| Load Capacity | 500 - 1700 kg | 1500 - 3500 kg | 3000 - 6000 kg | |
| Actuator | Electromagnetic Actuator | |||
| Maximum Actuator Force | Vertical: 40 N, Horizontal: 20 N | Vertical: 80 N, Horizontal: 40 N | ||
| Degrees of Freedom | 6 degrees | |||
| Active Isolation Range | 0.5 - 100 Hz | |||
| Vibration Isolation at 1 Hz | ≥90% | |||
| Input Voltage (V) | AC100 - 240V / 50 - 60 Hz / 1A | |||
| Power Consumption (W) | Maximum 110W, <50 W in normal operation | |||
| Operating Range | Temperature (°C) | 5 - 50 °C | ||
| Humidity (%) | 20 - 90% | |||
| Required Air Pressure | ≥ 0.5 MPa (≥ 5 bar) | |||
4. Summary
| Floor Vibration Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 1 - 80 Hz | ||
| Floor Vibration Specification | VC-E | VC-E | VC-E |
| Measurement Direction | Z axis (Vertical) | X axis (Left to Right) | Y axis (Front to Back) |
| Floor Vibration | Fail | Fail | Fail |
| Vibration On Active Vibration Isolation System | Pass | Pass | Pass |
5. Results – Vibration Criterion Curves
VC Curves, Z-axis (Vertical)
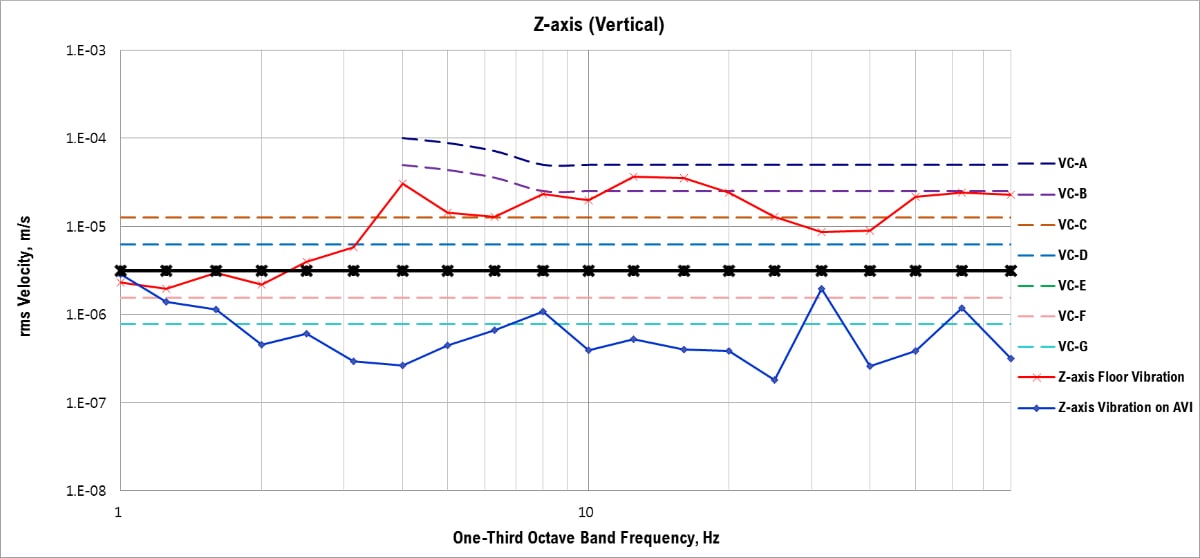
AVI = Active Vibration Isolation
The measured vertical floor vibration did not meet the vibration specification VC-E.
The active vibration isolation system reduced the vertical floor vibration from VC-A to VC-E.
VC Curves, X-axis (Left to Right)
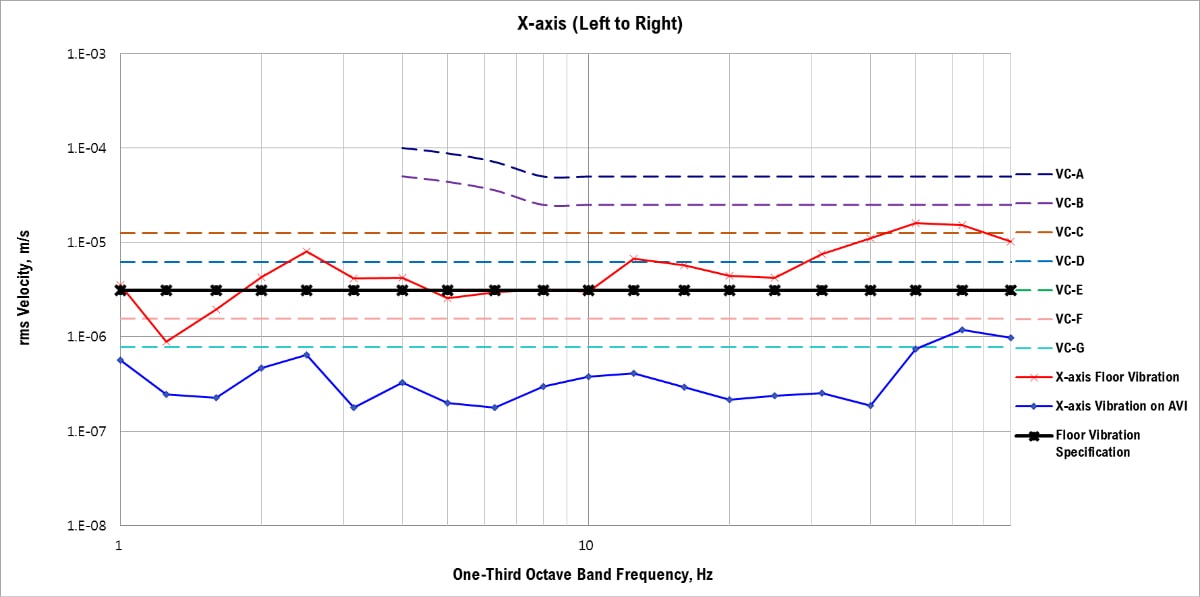
AVI = Active Vibration Isolation
The measured X-axis floor vibration did not meet the floor vibration specification VC-B.
The active vibration isolation system reduced the X-axis floor vibration from VC-B to VC-F.
VC Curves, Y-axis (Front to Back)
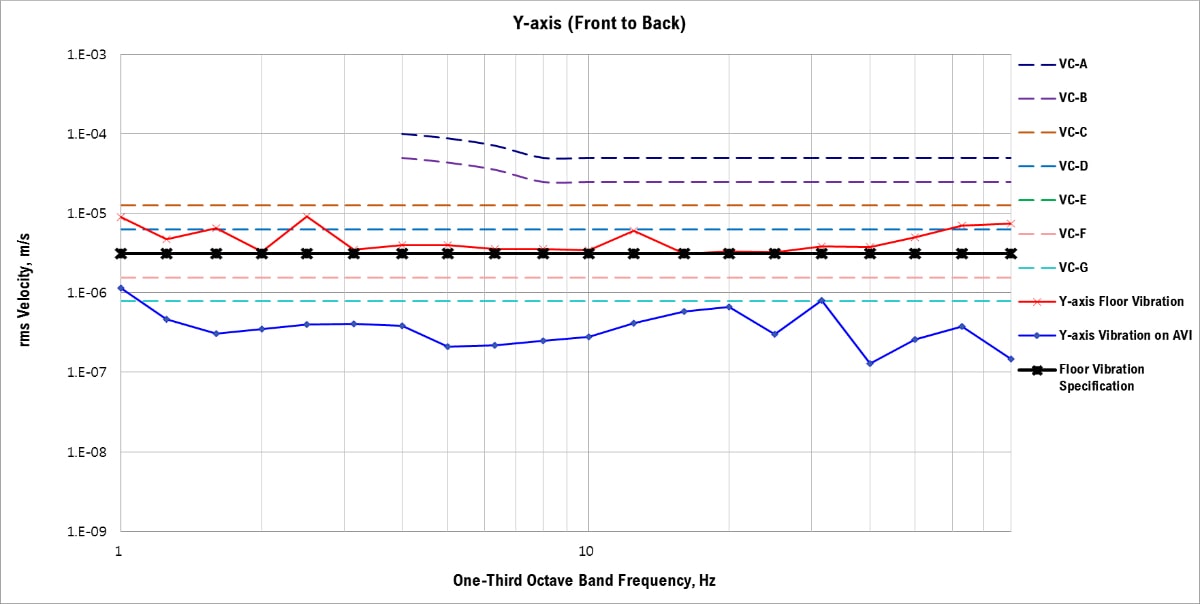
AVI = Active Vibration Isolation
The measured Y-axis floor vibration did not meet the floor vibration specification VC-C.
The active vibration isolation system reduced the Y-axis floor vibration from VC-C to VC-G.
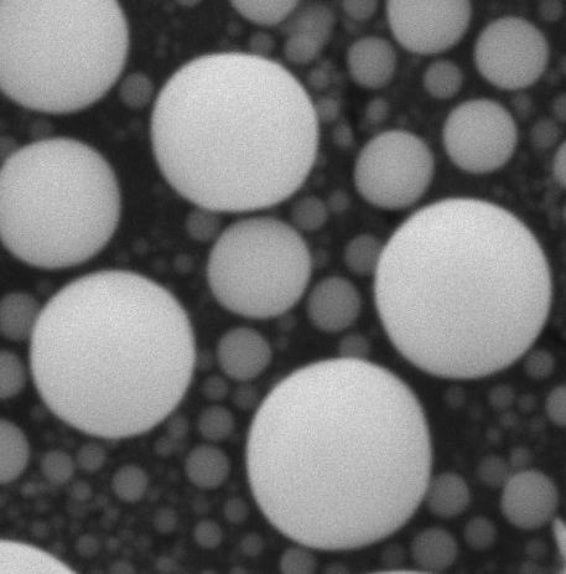
6. Results – Active Isolation Off vs Active Isolation On

Active Vibration Isolation Off
HV:15.00 kV
Mag: 50 000 x
Linewidth: 1 μm
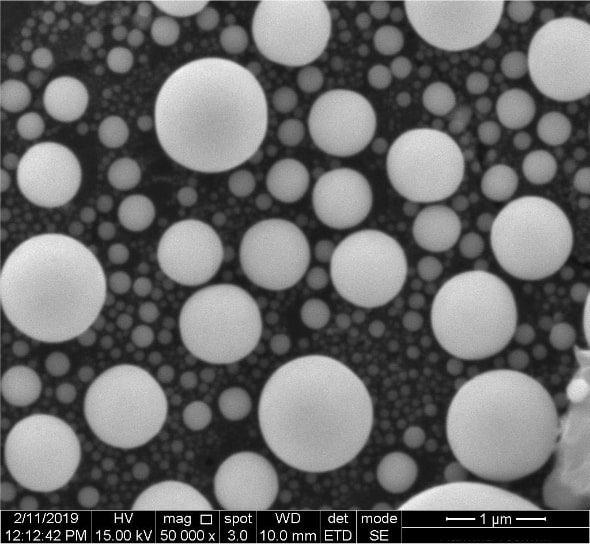
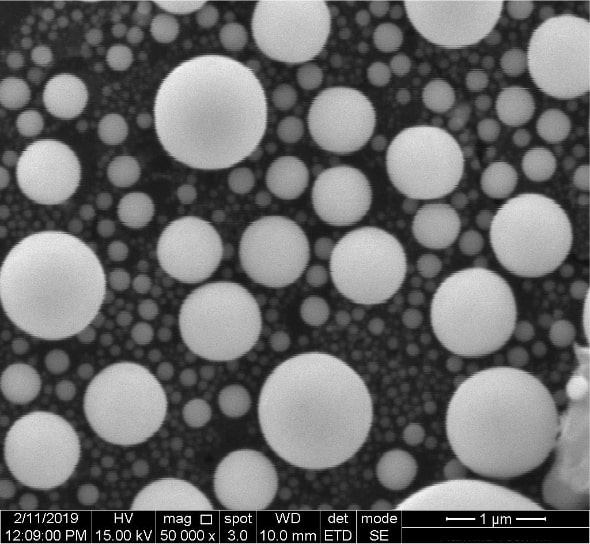
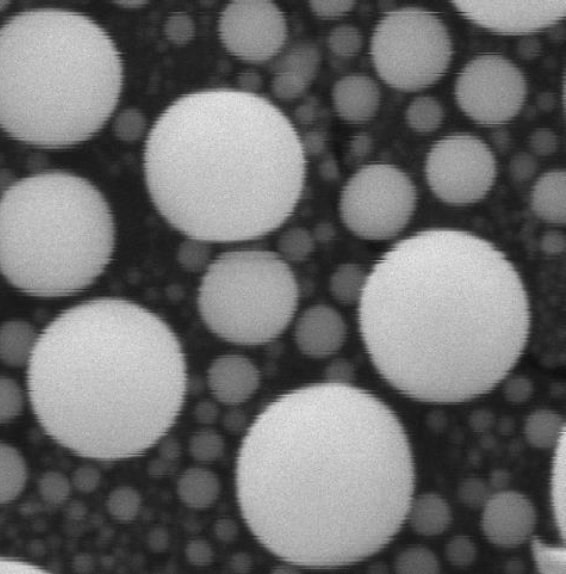
Active Vibration Isolation On
HV:15.00 kV
Mag: 50 000 x
Linewidth: 1 μm
Active Vibration Isolation Off
HV:15.00 kV
Mag: 50 000 x
Linewidth: 1 μm

Active Vibration Isolation On
HV:15.00 kV
Mag: 50 000 x
Linewidth: 1 μm
7. Reference
Generic Vibration Criteria
| Criterion Curve | Description | Amplitude1) μm/s (in/s) | Detail Size2) μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workshop (ISO) | Distinctly perceptible vibration, Appropriate to workshops and non-sensitive areas. | 800 (32,000) | N/A |
| Office (ISO) | Perceptible vibration. Appropriate to offices and non-sensitive areas. | 400 (16,000) | N/A |
| Residential Area (ISO) | Barely perceptible vibration. Appropriate to sleep areas in most instances. Usually adequate for computer equipment, hospital recovery rooms, semiconductor probe test equipment, and microscopes less than 40x. | 200 (8,000) | 75 |
| Operating Theatre (ISO) | Vibration not perceptible. Suitable in most instances for surgical suites, microscopes to 100x and for other equipment of low sensitivity. | 100 (4,000) | 25 |
| VC-A | Adequate in most instances for optical microscopes to 400x, microbalances, optical balances, proximity and projection aligners, etc. | 50 (2,000) | 8 |
| VC-B | Appropriate for inspection and lithography equipment (including steppers) to 3pm line widths. | 25 (1,000) | 3 |
| VC-C | Appropriate standard for optical microscopes to 1000x, lithography and inspection equipment (including moderately sensitive electron microscopes) to 1μm detail size, TFT-LCD stepper/scanner processes. | 12.5 (500) | 1-3 |
| VC-D | Suitable in most instances for demanding equipment, including many electron microscopes (SEMs and TEMs) and E-Beam systems. | 6.25 (250) | 0.1-0.3 |
| VC-E | A challenging criterion to achieve. Assumed to be adequate for the most demanding of sensitive systems including long path, laser-based, small target systems, E-Beam lithography systems working at nanometer scales, and other systems requiring extraordinary dynamic stability. | 3.12 (125) | <0.1 |
| VC-F | Appropriate for extremely quite research spaces; generally difficult to achieve in most instances, especially cleanrooms. Not recommended for use as a design criterion, only for evaluation. | 1.56(62.5) | N/A |
| VC-G | Appropriate for extremely quite research spaces; generally difficult to achieve in most instances, especially cleanrooms. Not recommended for use as a design criterion, only for evaluation. | 0.78(31.3) | N/A |
- As measured in one-third octave bands of frequency over the frequency 8 to 80 Hz (VC-A and VC-B) or 1 to 80 Hz (VC-C through VC-G).
- The detail size refers to line width in the case of microelectronics fabrication, the particle (cell) size in the case of medical and pharmaceutical research, etc, It is not relevant to imaging associated with probe technologies, AFMs, and nanotechnology.
The information given in this table is for guidance only. In most instances, it is recommended that the advice of someone knowledgeable about applications and vibration requirements of the equipment and processes be sought.








